Amateur radio programs for Android. Amateur radio programs for Android Let's start with the must-have application
Long introduction.
I have never been a passionate smartphone fan. Probably the main reason for indifference to these devices is their size and the lack of ability to work in a 3G network (my company has its own corporate connection with a very favorable tariffs for conversations, but not for the Internet). In addition, due to the nature of my work, I need to have my phone with me all the time and in rather dirty conditions, with a high probability of dropping it or knocking it somewhere. It’s inconvenient for me to put my phone in different plastic bags, silicones, and cases, since I’m used to carrying my phone in my pockets. For this reason my old Sony Ericsson The K750 has been with me for several years now and there was no reason to replace it.
But then they send me on a business trip, and after it, I immediately go to a sanatorium to relax. In both places there were rather dubious options for accessing a computer, but free WiFi was promised in both hotels. Since I can’t abandon my Internet resources for such a long time, and I didn’t want to carry a laptop around with me at all, I decided to take a Google phone with me. And therefore, from his wife, amid dissatisfied exclamations :), he was taken away Galaxy Gio, and in return I was given my old Sony Ericsson.
To be honest, I liked Galaxy Gio even earlier because of its adequate dimensions and low price. And it was me who initiated the replacement of my wife’s old, dead folding phone with a Galaxy Gio.
Before the business trip, my acquaintance with Galaxy Gio was rather superficial - set up WiFi, account, some other little things... after the sanatorium, based on some experience with the phone, I came to the following conclusions:
— the phone’s dimensions are convenient (due to the fact that it is thinner than my Sonyerikson) and is even less of a nuisance in your pocket;
- synchronizing contacts with a Google account is a good thing (I was tired of transferring contacts via Bluetooth from the old phone to the new one), the loss of the phone will no longer be so catastrophic, since the contacts (the most valuable thing in the phone) are stored in the Google account;
— working on the network (in Opera), in principle, is tolerable, but the functionality is rather limited, which creates problems, for example, if you need to do something more than answer an email or post in a forum;
- enter text on touchpad undeniably more convenient than on a regular phone, but nothing can replace a regular keyboard and mouse;
- The gluttony of the phone is very annoying! Daily exercise is required. And since I had to schlep around on trains and make long journeys, I developed a strong instinct to save the battery (it’s good that there is a separate player, otherwise I can’t play games or listen to music on the road, because at the end of the journey you can easily be left without communication) . You also constantly carry a charger with you and look for an outlet at every station to plug into (before the smartphone, I perceived McDonald’s only as a place where you could have a snack in an unfamiliar city - now they have another function :)).
In general, in the end, despite certain shortcomings, I decided to keep the Galaxy Gio for permanent use (my wife bought the same one, only white :))
Closer to the point.
Why such a long introduction? But to no avail! It was me who finally got to my computer and started scribbling text :). And in this article I wanted to talk about applications for Android that could be useful in the development of electronic devices.
It must be said right away that, due to the specifics of the Google Phone (it is, after all, a phone), you can’t count on anything serious, but what is there, we’re happy about it.
After wandering around on Google Play Store I have made a small selection, which, in my opinion, may be useful to you. The selection does not claim to be complete and if you know any interesting applications- write, I’ll add.
1 LET'S START FROM THE MUST-HAVE APPLICATION.
The Market has both paid and free version applications. Much respect to the author for the fact that the free version is almost completely functional (except for the absence of individual sections and the presence of advertising).
2 GROUP OF ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT SIMULATORS.


An ascetic, without any settings, and according to the creators, a fast (High performance native code using OpenGL ES 2.0) spectrum analyzer. The declared range is 20 – 22,000 Hz, but we understand that it will be significantly narrower. The scale is logarithmic. Based on my testing, it's pretty accurate.
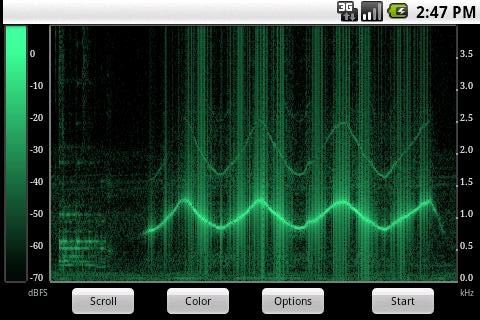

Another spectrum analyzer, but compared to the previous one, it does not just display the spectrum, but draws it in time. It turns out quite clearly. In the free version, the frequency range is limited to 8 kHz and the scale is linear. The paid version removes frequency restrictions, adds color schemes, and allows you to choose the scale type
4 GROUP OF GENERATORS.
Close in meaning to the previous group, but, it seems to me, more in demand. Again we can only count on an output range of 20 – 22,000 Hz. The signal can be sent to a speaker or through the audio jack (and amplifier, if necessary). There is only one application in this group so far, but it is very functional.
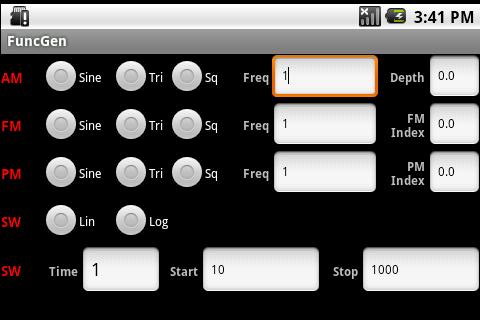

Quite a functional free generator. It can produce sine, square, saw, “white” and “pink” noise. For meander and saw, the duty cycle can change. In addition, it can create a signal with amplitude, frequency and phase modulation (and the modulating signal can also be a sine wave, square wave or sawtooth). The program can also automatically increase/decrease the frequency over time linearly or logarithmically. Everything is convenient, simple, and most importantly, there is no sticky attenuator handle, which developers love to stick into such programs.
5 GROUP FOR AVR DEVELOPER.


Currently, it is difficult to keep up with the latest radio electronics technologies. A variety of electronic devices can now be modified to suit your taste from one to another. There would be desire and ability. Even from an old electronic clock you can make a simple tester for many electrical circuit parts, not to mention tablets and computers. Many radio amateurs and professionals often have to use accurate electronic devices, among which the oscilloscope is very popular. Such a good device is not cheap. Although making it yourself using a tablet and Android will not be difficult even for a radio amateur.
What is an oscilloscope and its functions
 For those who are not particularly familiar with the operation of an oscilloscope and its visual views, I will explain. This is a device (in the old version like a mini-TV, in the new version - a tablet design, etc.) that measures and tracks frequency fluctuations in the electrical network. In practice, it is widely used by many specialized laboratories and professional radio broadcasters. Since precise settings of many electrical appliances are made only with its help.
For those who are not particularly familiar with the operation of an oscilloscope and its visual views, I will explain. This is a device (in the old version like a mini-TV, in the new version - a tablet design, etc.) that measures and tracks frequency fluctuations in the electrical network. In practice, it is widely used by many specialized laboratories and professional radio broadcasters. Since precise settings of many electrical appliances are made only with its help.
Its readings in electronic or paper form allow you to see sinusoidal waveforms. The frequency and intensity of this signal, in turn, allows determine the malfunction or incorrect assembly of the electrical circuit. Today we will look at a two-channel oscilloscope, which you can assemble with your own hands based on the existing circuits of a smartphone, tablet and the corresponding software.
Assembling a pocket oscilloscope based on Android
The measured frequency must be audible to the human ear, and the signal level must not exceed standard microphone sound. In this case, you can assemble an Android-based oscilloscope with your own hands without additional modules. Disassembling the headset, on which there is a microphone. If you do not have this headset, you will need to purchase a 3.5 mm audio plug with four contacts. Solder the probes according to the connectors of your gadget.
Download software from the Market that will measure the frequency of the microphone input and draw a graph based on this signal. The presented options will be enough to choose the best one. After calibrating the application, the oscilloscope will be ready for use.
Pros and cons of the “Android” build:

Assembling an oscilloscope from a tablet
To stabilize the signal and expand the input voltage range, you can use an oscilloscope circuit for a tablet. It has been used for a long time and successfully to assemble devices for the computer.
For this purpose, KS 119 A zener diodes with resistors of 10 and 100 kOhm are used. The first resistor and zener diodes are connected in parallel. Second and more powerful resistor connected to the input of the electrical circuit. This expands the maximum voltage range. Ultimately, additional interference disappears and the voltage increases to 12 volts.
A special feature of the tablet oscilloscope is that it works directly with sound pulses and unnecessary interference (shielding) of the circuit and probes in this case will be undesirable.
Necessary software for assembling an oscilloscope based on a tablet and Android
To work with such a circuit, you will need a program that can draw graphs based on the incoming audio signal. Many such options can be easily found in the Market. With their help you can select additional calibration and achieve maximum accuracy for a professional oscilloscope from a tablet or other functional device.
Wideband frequency using a separate gadget
 A wide range of frequencies using a separate gadget is achieved by its set-top box with an analog-to-digital converter, which provides signal transmission in digital version. Due to this, higher measurement accuracy is achieved. In practice, it is a portable display that accumulates information from individual devices.
A wide range of frequencies using a separate gadget is achieved by its set-top box with an analog-to-digital converter, which provides signal transmission in digital version. Due to this, higher measurement accuracy is achieved. In practice, it is a portable display that accumulates information from individual devices.
Oscilloscope from an Android tablet
Bluetooth channel
Currently, with electronic progress, consoles appear in stores that perform the functions of an oscilloscope. They transmit a signal using a Bluetooth channel to a tablet or smartphone. Such an oscilloscope is an attachment, connected to tablet via Bluetooth has its own characteristics. The measured frequency limit of 1 MHz, the probe voltage of 10 V and the range of about 10 meters are not always sufficient for the professional range of work activities. In such cases, you can use an oscilloscope - a set-top box with data transmission using Wi-Fi.
Transfer data using Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi significantly expands the capabilities of measuring devices. This type of information exchange between the tablet and the set-top box is especially popular. This is not a fashion statement, but pure practicality. Since the measured information is transmitted without delay to the tablet, which instantly displays any graph on its monitor.
 A clear user menu allows you to quickly and easily navigate controls and settings electronic device. A recording device allows you to reproduce and transmit information in real time and to all points for all participants in this process.
A clear user menu allows you to quickly and easily navigate controls and settings electronic device. A recording device allows you to reproduce and transmit information in real time and to all points for all participants in this process.
Usually, along with the purchased oscilloscope set-top box, a disk with software is supplied. These drivers and program You can quickly download it to your tablet or smartphone. If there is no such disk, find this data in the application store or search on the Internet on forums and specialized sites.
DIY USB oscilloscope circuit diagram
Assembling a USB oscilloscope will cost you only 250–300 rubles and you can make it yourself.

The advantages of this device are its low cost, mobility and small size. But, unfortunately, there are more significant disadvantages. These are low sampling rate, presence of a PC, low bandwidth and memory depth.
For professionals this electronic “toy” obviously won't do. And for beginner radio amateurs, this is a very good oscilloscope simulator for acquiring certain practical skills.
Tablet computers and smartphones, when used correctly, become indispensable assistants V professional activity electricians. Moreover, we are talking not only about storing contacts or communicating with colleagues, but also about assistance directly during measurements.
Modern measuring instruments often have built-in computers that process, store and organize data. At the same time, electricians also carry very powerful computing devices, which are smartphones and tablet computers. These mobile gadgets are used in professional activities for communication, database storage, data and GPS navigation. But their capabilities are much wider and it would be useful to use smartphones and tablets to work with measurement results.
This provides the following main advantages:
- reducing the total cost and total weight of the equipment available to the electrician;
- the presence of different data in one device, for example, the geographical location of an object and the measurement results on it;
- there is no need for additional training, since the mobile device has a user interface that is already familiar to the employee.
Using a Bluetooth adapter
Mobile devices have wireless interfaces. By connecting the measuring device to a smartphone or tablet computer through such an interface and installing special software on the computer, you can get a mobile measuring system.
But here comes the problem. The fact is that measuring devices are still equipped with an IR interface, not Bluetooth. And the reason here is not only that the developers of measuring equipment are characterized by some conservatism. To exchange data between devices in the measuring complex, the RS-232C interface is usually used (known to users personal computers as "COM port"), which is easily implemented in the simplest scheme IR adapter. To implement RS-232C via Bluetooth, a software implementation of a virtual COM port is required, which significantly complicates and increases the cost of the equipment.
However, it has been almost 10 years since the IR interface fell out of use in mobile computing. How then to connect them with measuring instruments? The problem is so pressing that when Agilent Technologies released the U1177A IR-Bluetooth adapter that solved it in 2013, this product was immediately awarded the title “Product of the Year” by the authoritative American magazine Electrical Constructions & Maintenance.
The U1177A adapter is designed to work with Agilent Technologies U1230, U1240, U1250 and U1270 series digital multimeters, as well as U1210 series current clamps.
The device, measuring only 39x71x37 mm and weighing 60 g, is mounted on the back of the multimeter (U1240 series multimeters require a special bracket, purchased separately), its IR sensor is applied to the IR port window of the measuring device. The adapter supports the Bluetooth 2.1 protocol, the communication range can reach 10 m. The U1177A is powered by two AAA elements, which are enough for 30 hours of operation.
For the U1177A adapter, Agilent Technologies has developed two free apps on Android platform: Mobile Logger and Mobile Meter. The first of them allows you to build graphs of changes in parameters, as well as send SMS or e-mail when specified events occur. By the way, Mobile Logger is also available for computers running Windows, as a plug-in for standard Agilent Technologies software. The second application allows you to simultaneously monitor measurement data from three devices. A very valuable feature that allows you to avoid running from device to device and not placing an assistant next to one of the multimeters so that he reports measurement data. Both applications are capable of running on both smartphones and tablet computers, however, for Mobile Logger, a tablet is preferable due to its larger screen size.
The CEM company produces an industrial professional multimeter DT-9979, equipped with a built-in Bluetooth module. The Meterbox application is installed on the Android device that is used in conjunction with the CEM DT-9979. In the event that a high-speed Internet connection cannot be established or this option is disabled by the user, the program performs statistical processing on the local mobile device. If there is an active high-speed Internet connection, they will automatically connect cloud services. The data is sent to the cloud, where it is processed using more complex algorithms than on a local device. Cloud services allow you to transfer to new level interaction of several specialists, as well as control in the company where such measuring instruments are used. Measurement data is recorded and stored in the “cloud”; if necessary, a manager or other authorized specialist can easily access it from any place where there is an Internet connection.
Oscilloscopes based on Android devices
The so-called USB oscilloscopes have long been known, in which signal processing is carried out mainly by a computer, and its display is also used to display information. With data transfer rates for the USB 2.0 interface up to 480 Mbit/s, and in more modern USB versions 3.0 - up to 5 Gbit/s, no problems arise with transferring information from the external unit to the computer.
In order to connect a USB oscilloscope to a tablet computer or smartphone, the mobile computer must have a full USB port (host). The vast majority of smartphones and tablets do not have such a port; the oscilloscope can connect to them via Bluetooth and Wi-Fi interfaces.
Wi-Fi-enabled oscilloscopes are available, but their software is only designed to run on the operating systems used on desktop and laptop computers. This is due to the high cost of such oscilloscopes, which limits their scope of application mainly to car repair shops.
A less expensive option is an oscilloscope with Bluetooth. But here the problem arises of low data transfer speed through this interface. Theoretically, it does not exceed 24 Mbit/s, but practically in most devices it is 1–2 Mbit/s. This gave rise to the opinion of some experts that it is impossible to create a good oscilloscope with a Bluetooth interface.
However, since 2009, enthusiasts in different parts of the world have created their own models of Bluetooth oscilloscopes, fortunately, element base This is what it existed for. And, finally, in 2013, the small Hungarian company E-Way+ began serial production of the BlueDSO oscilloscope with USB and Bluetooth interfaces.
The disadvantage of this oscilloscope, apparently due to the low bandwidth of the Bluetooth interface, is the inability to fully operate with frequencies above 1 MHz. For radio applications this is a serious problem. But for practical use in electrical engineering, frequency bands up to 1 MHz are quite sufficient.
BlueDSO fits in the palm of your hand. Unfortunately, it does not have autonomous power supply; when working with a desktop computer or laptop, power is supplied via USB. When working with a mobile computer via Bluetooth, you must connect a USB power supply to the device.
The portable oscilloscope-multimeter CEM DT-9989 has a Bluetooth interface. This self-powered oscilloscope is a self-contained device with a built-in display. Signal processing occurs mainly inside the oscilloscope, which allows data to be transmitted via Bluetooth at a speed of only 9.6 kbps with an operating frequency band of up to 10 MHz. Cloud services are also available for the CEM DT-9989 via the Meterbox app.
Oscilloscope based on iOS devices
The American company Oscium produces two models of oscilloscope attachments - iMSO-104 and iMSO-204, which connect to Apple iPhone And Apple iPad via the docking station connector. The operating frequency band reaches 5 MHz. The iMSO-104 has one and the iMSO-204 has two analog channels. In addition, the set-top boxes have 4 digital channels.
Oscilloscopes obtained by connecting an Apple iPad and an Oscium set-top box can take “snapshots” of the screen and send them by e-mail, and carry out mathematical processing of measurement results.
Screenshots can be sent to management for a report or, for example, for consultation with a more experienced specialist. Disadvantages of Oscium products include a small range of input voltages (from –40 to +40 V) and the absence of a current measurement mode. At the same time, non-standard input connectors do not allow connecting accessories that reduce the measured voltage.
Using mobile device sensors
The sets of consoles and corresponding software described in the article are united by the fact that nodes are added to the computer, on which the accuracy of the measurement depends. In this case, this is an analog-to-digital converter, precision voltage dividers, shunt resistors, etc.
In addition, there are a considerable number of programs that take measurements using sensors built into a mobile computer.
For example, it is proposed to measure using mobile device:
- magnetic induction (which allows you to search for objects made of magnetic metals located at a distance of up to 3 cm from the smartphone, based on the increase in magnetic induction when approaching them);
- noise level;
- illumination
For these measurements, the built-in compass, microphone and camera of the mobile device are used, respectively.
It should be noted that these types of programs can only give a very rough estimate. Therefore, they should not be used in professional electrician activities. At the everyday level, you can evaluate whether it makes sense to complain to local authorities about noise from construction or insufficiently lit streets. But even with this use, the programs will give any reliable estimate only if they have been calibrated using a professional device. Otherwise, the obtained data may differ several times from the real ones, since the spread of component parameters, for example, in a smartphone, is much greater than in a specialized measuring instrument. For example, experience using one of the iPhone light meter programs without calibration showed that it can give measurement results that differ by up to 4 times from real values.
Therefore, programs that carry out measurements with the built-in sensors of a mobile device are useful mainly as an illustration of the laws of physics, as a means of introducing the general public to scientific and engineering activities. But to carry out measurements for professional purposes, additional devices must be connected to the computer.
Alexey VASILIEV
A smartphone or tablet equipped with a camera can be of benefit to an electrician without installing any applications. By pointing the camera of a mobile device at a light source, you can detect pulsations that are invisible to the naked eye, but nevertheless have a negative effect on a person. If the ripple factor is more than 5%, the image will flicker on the device display. This property of a digital camera turns out to be very useful, for example, when choosing LED lamps. Ask the seller to show how the lamp shines and check it for pulsation using your smartphone.
Review of amateur radio programs for Android devices
Good afternoon, dear Radio Amateurs!
Today on the website, we will consider a rather interesting question - amateur radio programs for devices running Android OS.
Recently, the electronic equipment market has been filling up at a good pace with inexpensive (mostly Chinese, but fairly decent quality) devices that use operating system Android. You can already buy a good tablet for 5,000 rubles. Therefore, I was interested in the question: are there amateur radio programs for such devices? It turns out there is, and not a little. Below I will give you an overview of several such programs, and we will look at one of them in more detail.
So, the first program is OscilPrime Oscilloscope Legacy
This program allows you to turn your tablet computer into a two-channel low frequency oscilloscope:
The signal under study can be supplied to the audio connector and through USB port. In addition, the program has a built-in sinusoidal signal generator. The sweep can be triggered either by the decline of the signal under study or by its edge. The program is easy to use and has limited settings.
Next program – EveryCircuit(paid – 300 rubles) or EveryCircuit Free(free).
This program allows you to assemble simple radio circuits on the tablet screen and simulate their operation:

The program is simple and not difficult to understand. As a disadvantage, we can note the lack of “Russian language”, a small base of elements and the high cost of the full version. But despite the shortcomings, the program will allow you to think through some aspects of circuit design when building simple devices.
As you can see, dear radio amateurs, progress does not stand still, programmers take care of us and release new programs. Even if they are not yet as developed as for “big” computers, I think that soon “small” computers will catch up with their “big brothers” in amateur radio software.
You can download all these programs (and not only them) through the “Play Market” on your gadget.
And finally, I want to introduce you to another amateur radio program that deserves close attention, and not only by beginning radio amateurs.
The program is called ElectroDroid.
There are both paid and free versions of this program. The difference between the paid version is that additional features and there are no annoying ads.
ElectroDroid is a powerful toolkit and reference for the electronics developer:

The program consists of several sections:
– calculation
– pinout
– directory
– plugins
Let's start from the end - plugins. This function allows you to expand the capabilities of the program by adding new functions. All new plugins are installed within the program.
Calculation – this section Designed for various amateur radio calculations. In the top picture you can see almost all the program's capabilities in this mode (some are hidden at the bottom). As you can see, there is quite a wide variety of small subroutines for carrying out simple, but at the same time useful amateur radio calculations.
Tsokolevka. This section of the program presents the pinout of the most popular and frequently used connectors, wires and devices in amateur radio practice:

Directory. This section presents various reference data on radio elements, as well as tables of various data needed in amateur radio practice. This section will especially please fans of PIC microcontrollers - reference data on almost all PIC microcontrollers is collected here (it’s a pity, of course, that there is no such reference book on AVR microcontrollers):

You can also download this program from the Play Market, or (using the services of our hackers) download full version of this program below:
(1.9 MiB, 10,325 hits)
This application has only been tested with Samsung Galaxy GT-i5700 Spica (Android 2.1)
The circuit uses a PIC33FJ16GS504 Microchip (datasheet) as an ADC for two inputs. The processed data is transferred to the phone via the Bluetooth module LMX9838 (datasheet).
Oscilloscope characteristics:
– Division time: 5μs, 10μs, 20μs, 50μs, 100μs, 200μs, 500μs, 1ms, 2ms, 5ms, 10ms, 20ms, 50ms.
– Volts per division: 10mV, 20mV, 50mV, 100mV, 200mV, 500mV, 1V, 2V, GND
– Analog input (preamp dependent): -8V to +8 V
The source codes for Bluetooth were taken from http://developer.android.com. This example consists of three Java source code files. And I completely copied "DeviceListActivity.java" which is used to search for remote Bluetooth devices. I changed "BluetoothChatService.java", removing everything unnecessary from there.

The rest of the work mainly consisted of transferring my previous developments for the S60 to Java. It was difficult, but nevertheless, it was good example to learn JAVA programming.
Source codes and firmware for Android and PIC can be downloaded.
Here's the diagram. There is nothing special about it, everything is based on existing schemes.

Perhaps I did not choose the best microcontroller for this purpose, because... there were unused conclusions. But I was only able to buy this one and it’s the best ADC.
If you want to change the input voltage range by changing the op amp preamp, the calculation is in the "adc.xmcd" file. Also, besides LMX, you can use other Bluetooth modules.
Original article on English(translation: Ivan for the site cxem.net)



